LECTURES
The scientist’s professional activities were associated with the Imperial University of Warsaw, where he headed the department of the faculty therapeutic clinic (1895-1910), was the dean of the medical faculty and acting as the rector (1909-1910). Professor Kudrevetski V.V. was a scholar of an outstanding scientist, academician Pavlov I.P. Under his leadership in a small laboratory of the prof. S.P. Botkin clinic, they carried out the first fundamental research and experimental work on the physiology of digestion. The accumulated experience on this topic allowed Kudrevetski to defend his doctoral dissertation in 1890, the scientific consultant of which was Ivan Petrovich himself. The results of fundamental works of V.V. Kudrevetski formed the basis of scientific ideas about the physiology of the digestive system and have not lost their relevance today.
REVIEW ARTICLES
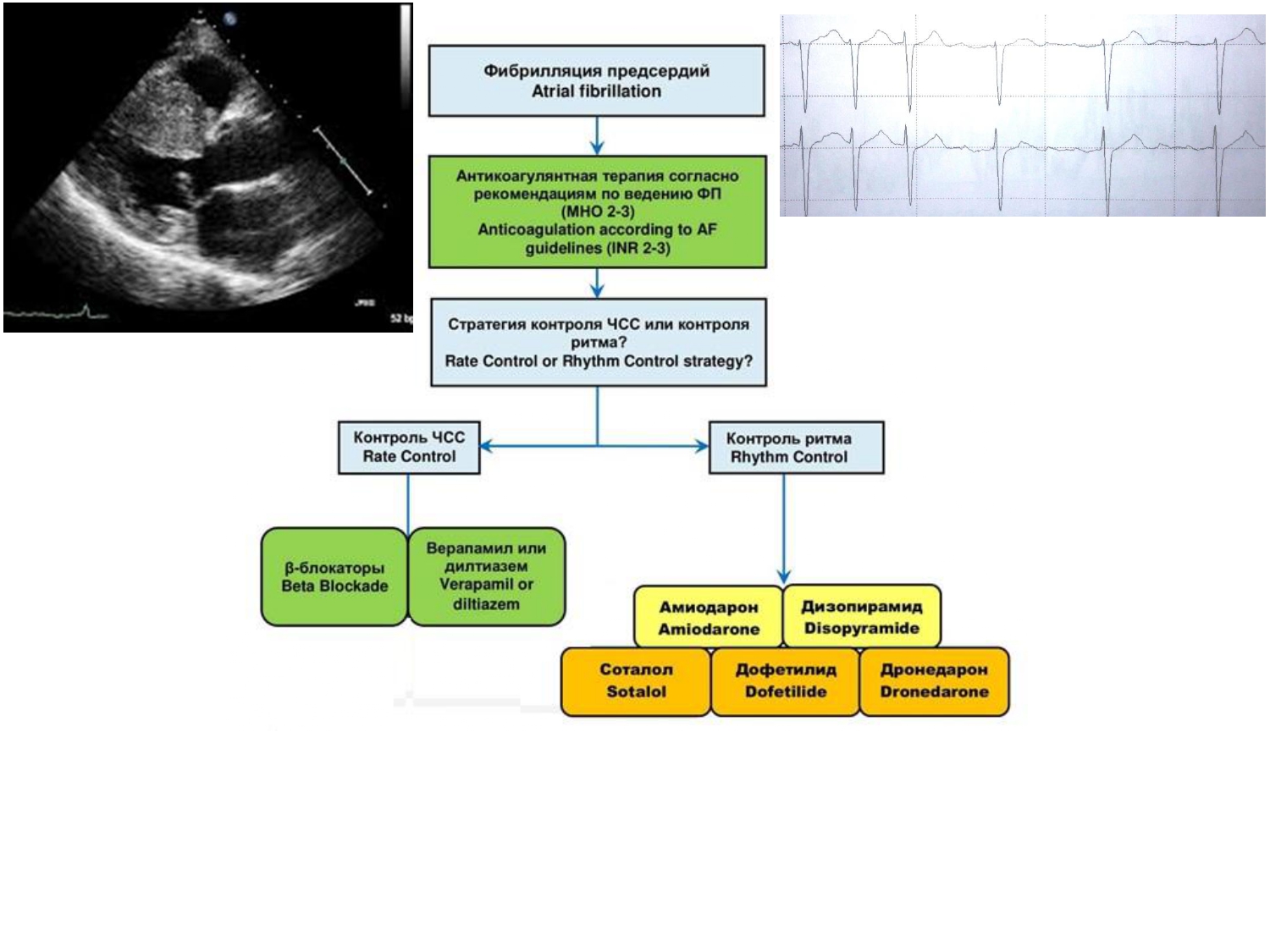
The current information about features of atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is presented in this review. The data about prevalence, pathogenesis and its various complications in these patients are disclosed. The article contains updated clinical recommendations of authoritative medical societies on the discussing problem. There is detailed discussion of risk factors of atrial fibrillation onset in setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with demonstration of results of different studies concerning to investigation of relationship between risk factors and probability of the arrhythmia development. There is description of detection methods, clinical manifestations, and the course of atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The contemporary literature data are presented regarding to the management of patients with atrial fibrillation with use of anticoagulants, antiarrhythmic drugs, indications for performing of radiofrequency ablation and results of studies concerning long-term efficacy of such procedure are demonstrated. The discussion on the management of the patients in cases of sinus rhythm restoration or maintenance failure is described.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has proven to be a major global public health crisis, as evidenced by the steady increase in re-infected patients. In spite of the fight against this infection going on for more than a year, the unpredictable consequences of COVID-19, with or without concomitant chronic diseases, are still insufficiently studied, which undoubtedly is an additional burden on the outpatient health care unit. This article is a review of the available modern literature on the features of the course and duration of the post-COVID period. More than fifteen studies have been analyzed, in which the authors evaluated the incidence of symptoms in post-COVID period and its clinical characteristics.
This review highlights the relationship of age and arterial hypertension observed in the aging process. The main structural and functional changes underlying the increase in vascular stiffness are analyzed. The similarity of vascular changes in aging and arterial hypertension was noted. The negative effect of increased central blood pressure on target organs is considered. Attention is paid to the analysis of arterial stiffness as a marker of vascular aging. The parameters of the carotid-femoral pulse wave propagation velocity, the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI), the ankle-brachial index, the finger-brachial index, and the augmentation index were examined separately. The prognostic and clinical value of the parameters of vascular stiffness is considered. In particular, the clinical guidelines for arterial hypertension report the need to use arterial stiffness indicators to improve the accuracy of cardiovascular risk stratification, especially in medium-risk patients. Measurement of vascular stiffness and central aortic pressure should be recommended as one of the methods for stratifying cardiovascular risk in patients with intermediate SCORE risk, as well as in those whose target organ damage was not detected by routine methods. The article also notes the independent diagnostic and prognostic value of the CAVI.
Damage to the meninges in combination with the presence of a defect in the bone structures of the base of the skull and the formation of communication with the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses are necessary conditions for nasal liquorrhea. There are a number of complications of nasal liquorrhea of various origins: infectious (meningitis, brain abscess), pneumocephalus, aspiration pneumonitis and gastritis. A review of the literature related to aspiration pneumonitis in nasal liquorrhea has been carried out. 4 articles were selected with descriptions of 9 cases. The analysis of demographic indicators of patients, clinical data, treatment characteristics was carried out. Based on the analysis of the literature, aspiration pneumonitis is a rare complication of nasal liquorrhea. For differential diagnosis with other types of pneumonitis, it is necessary to rely on additional clinical data, such as unilateral discharge of clear fluid from the nose when tilting the head, worsening of the condition and intensification of symptoms in a horizontal position, absence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, ineffectiveness of antibiotic therapy, recurrent the nature of the flow. Antibiotic therapy does not cure the patient from pneumonitis. For the treatment of this pathology, it is first of all necessary to eliminate the cause of aspiration — to perform plastic surgery of the skull base defect in the absence of contraindications from the side of anesthetic aid.
In the modern world the problem of obesity in combination with new coronavirus infection has acquired a special danger. On the one hand, the prevalence of obesity among the population is steadily increasing, on the other-it has been proven that obese people are among the most vulnerable in terms of increased risk of infection and a serious prognosis. This is due to the presence and peculiarities of the development of various pathological mechanisms in this category of patients. These include: high expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, a high probability of a «cytokine storm» developing, maintenance of a chronic inflammatory process in adipose tissue, changes in the activity of Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme. All these processes lead to an aggravation of metabolic disorders in adipose tissue and violation of immune protection. The world medical practice in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic shows that patients with coronavirus infection against the background of obesity more often need hospitalization in intensive care units and connection to artificial ventilation equipment. Currently, many features of the course of coronavirus infection against the background of obesity have been identified and continue to be studied. These include: the presence of severe respiratory failure, a high risk of developing respiratory distress syndrome, thrombosis and thromboembolic complications, as well as worsening of the course of chronic cardiovascular diseases. All this eventually leads to the development of severe multiple organ failure, which is often the cause of death in this category of patients.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The earliest correction of behavioral risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases will reduce the rates of premature mortality of the population. Currently, the relationship between the altered spectrum of intestinal microflora in various indicators of suboptimal health status and body mass index is not sufficiently studied. When they are in a state of suboptimal health status, patients consider themselves healthy and do not go to the doctor for a long time, which makes it difficult to implement early preventive measures in this group of patients. Goal. To determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of the intestinal microflora before and 1 month after taking a metaprebiotic complex containing dietary fiber (inulin) and oligosaccharides (oligofructose) in outpatient patients who consider themselves healthy, have behavioral risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases or chronic non-communicable diseases in remission, and/or do not consult a doctor within the last 3 months. Materials and methods. Outpatient patients were examined (114 people: 36 men, 78 women aged 18 to 72 years). A survey was conducted, including a detailed active collection of complaints (including using the international SHSQ-25 questionnaire) and anamnesis, as well as a thorough physical examination with an anthropometric study. Using the MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry method, the degree of microbiotic disorders, the structure of the intestinal microflora were determined with the identification of microorganisms isolated from feces before and after taking the course of the metaprebiotic complex with various indicators of suboptimal status and body mass index. Results. New data were obtained on the intestinal biocenosis of patients who consider themselves healthy at different levels of suboptimal status. When using a metaprebiotic complex containing inulin and oligofructose, an improvement in the composition of the intestinal microflora was found due to a decrease in the frequency of release of conditionally pathogenic enterobacteria and other gram-negative microorganisms (median degree of contamination: from 0.45 (0.3-0.98) to 0.3(0.21-0.7) at low suboptimal status and from 0.5(0.7-1.7) to 0.31 (0.2-1.3) at high) and increase the frequency of enterococcal excretion (median degree of contamination: from 5,58 (4,16-7,0) tо 6,3 (4,8-7,8) at low suboptimal status and from от 4,5 (2,8-6,3) tо 5,1 (3,8-6,4) at high). Conclusion. The importance of studying the microbiotic complex of the intestine in increasing the indicators of suboptimal health status and body mass index in patients who consider themselves healthy is proved, which will allow for the earliest detection and rational individual prevention of chronic non-communicable diseases.
ANALYSIS OF CLINICAL CASES
This article considers the relevance of treating psoriatic arthritis with genetically engineered drugs such as adalimumab and secukinumab. Also, it conducts retrospective analysis of the medical history of the patient, who had this therapy.
Introduction: Transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis is a severe rare disease with wide range of characters without specific symptoms including the damage to the peripheral nervous system and cardiac involvement. Case report: A 60-year-old female patient represented with weakness and paresthesia in the distal parts of the lower limbs, impeding walking for 2 years. Initially, symptoms were considered as a manifestation of degenerative stenosis of the lumbar spine, decompressive laminectomy was performed but the symptoms after surgical treatment persisted. Based on data from clinical and electroneuromyographic examinations, axonal sensorimotor polyneuropathy was diagnosed. Genetic testing of the patient, her elder sister, son and daughter using the Sanger sequencing method detected a variant of the nucleotide sequence in the fourth exon of the transthyretin gene (Chr18: 29178562, rs148538950, NM_000371.3: c.G368A: p. Arg123His) in the heterozygous state. A subcutaneous fatty tissue biopsy of abdominal wall with a Congo red stain and polarized light examination revealed amyloid microdeposits, grade CR 1+ (minimal deposits), confirmed the diagnosis of familial ATTR-amyloidosis. Echocardiography revealed concentric left ventricular wall thickening with normal end diastolic size and volume, preserved ejection fraction, left atrial enlargement, pulmonary hypertension and type 1 diastolic dysfunction. Specific anti-amyloid therapy — tafamidis was prescribed. Conclusion: In patients with peripheral polyneuropathy and left ventricular hypertrophy of unknown etiology, a complex examination is necessary for the timely detection and treatment of amyloid polyneuropathy and cardiomyopathy.
ISSN 2411-6564 (Online)