REVIEW ARTICLES
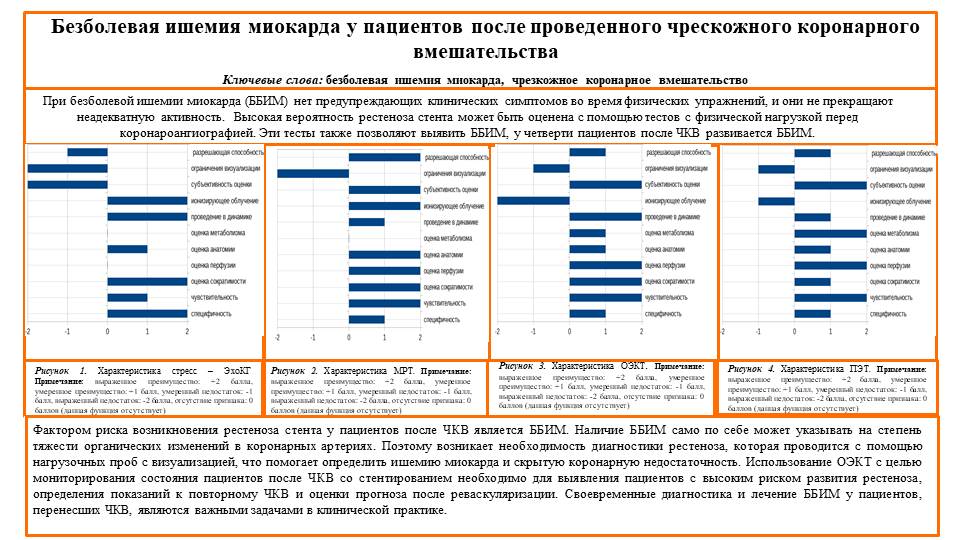
Frequency and timing of appearance of myocardial ischemia, including silent ischemia, were analyzed in published scientific sources. Silent myocardial ischemia is risk factor for stent restenosis after percutaneous coronary interventions. Patients with silent ischemia lack clinical symptoms while perfusion, metabolic and electrical activity of their myocardium may be compromised. These patients do not have warning clinical symptoms during physical exercise and do not stop inappropriate activity. Silent myocardial ischemia itself can indicate severity of atherosclerosis in coronary arteries. High probability of stent restenosis can be assessed by exercise tests prior to coronary angiography. These tests also allow to reveal clinically silent myocardial ischemia. Quarter of patients after coronary intervention develop silent myocardial ischemia. Silent myocardial infarction comprises 22-78 % of all infarctions after coronary interventions. Exercise tests based on single-photon emitting computed tomography can be used in diagnosing stent restenosis, silent ischemia and assessment of cardiovascular risk in patients after coronary interventions. Its results can be used as indications for repeated coronary interventions and for prognosis after revascularization. Exercise tests are recommended in two years after revascularization in absence of ischemic symptoms. Early tests are recommended in cases of high cardiovascular risk, suboptimal revascularization, stenting of arteries with small diameter or at bifurcation. Diagnosis of silent myocardial ischemia by single-photon emitting computed tomography in patients after coronary revascularization is significant for clinical practice.
In the first part we reviewed the issues of perioperative administration of steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, biologics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In this part we will discuss cardiovascular risks, prevention of infectious and thromboembolic complications and the impact of some structural alteration on the process of surgery and perioperative management.
In 35-56 % of patients depression of varying severity was diagnosed, in 25-76 % — anxiety and psychosexual disorders, in 40 % — anxiety and depressive disorders, in in 50 % — adjustment disorders, to 9.5 % — suicidal thoughts and attempts. Anxiety, depressive, dysmorphic and psychotic spectrum disorders are identified in 75 % of women seeking medical care during the menopause.
Psychopharmacotherapy in female patients includes modern antidepressants, anxiolytics, and antipsychotics, with an emphasis on good tolerability, compatibility with hormone therapy, and easy dosing.
Psychotherapy, psychological support and psychocorrectional work can reduce the severity of anxiety and depressive symptoms and significantly increase the success of treatment procedures.
The article presents modern views on the problem of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Data on the prevalence and risk factors for the development of the disease are presented. Emphasis is placed on the special role of slightly acidic and slightly alkaline reflux in the pathogenesis of GERD, which, in combination with dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter and impaired motor-evacuation function of the stomach, are important factors, determining the the lack of effectiveness of standard antisecretory therapy. The exceptional importance of the 24-hour pH impedanceometry method is emphasized for the differential diagnosis of the non-erosive form of GERD with functional heartburn and hypersensitivity of the esophagus to reflux (the so-called hypersensitive esophagus). The data of the results of domestic and foreign studies devoted to the evaluation of the effectiveness of the use of physiotherapeutic methods and drinking balneotherapy in patients with GERD are given.
The pathogenetic mechanisms of progression of chronic periodontitis accompanied with rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed by the common parts of immune-inflammatory reactions.
Damage to periodontal tissues is indirectly made by cytotoxic effects of enzymes and their metabolites produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis bacteria. Neutrophils contribute to the progression of periodontitis and participate in its amplification by recruiting T-helper cells 17 and contributing to the accumulation of plasma cells in the affected tissues. Activation of immunocompetent cells promotes the generation of reactive oxygen species that initiate free radical oxidation of lipids, which, combined with the inability to neutralize them due to reduced antioxidant potential, leads to the development of oxidative stress.
The connection between rheumatoid arthritis and chronic periodontitis has been the focus of numerous studies, due to their common pathogenetic mechanisms. Chronic inflammation associated with both rheumatoid arthritis and chronic periodontitis is similar in its prevailing adaptive immune phenotype, an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. The involvement of the Porphyromonas gingivalis microorganism in the generation of antibodies to citrullinated peptides in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is significant. The similarity of the epitope (SE) encoding the HLA-DRB1 allele, binding citrullinated peptides, can act as a basis for the approval of the genetic predisposition and mutual potential of these diseases. Thus, the proven connection between chronic periodontitis and rheumatoid polyarthropathies determines the significance of the analysis of the data obtained and substantiates the need for strategic research aimed at developing new methods in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the diseases for the purpose of breaking and separation of the common pathogenetic mechanisms of inflammatory reactions and osteoresorption processes leading to persistent functional and organic disorders.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The aim of the investigation was to study the relationship between the content of whole blood in mononuclear leukocytes in pneumonia and in apparently healthy individuals of cytokine signaling suppressor 2 (SOCS2) with the production of cytokines (TNFα, TGFb, IFNα, IFNβ, IFNγ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17A, RAIL-1, RANTES) and individual factors of the NF-kB and JAK / STAT signaling pathways (NF-kB2, p65, p50, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B, STAT6). Materials and research methods. The research material was mononuclear cells isolated from venous blood samples, as well as blood plasma of practically healthy individuals and patients with pneumonia. In nuclear-cytoplasmic lysates of mononuclear blood cells, the concentration of the components of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB, p65, p50, NF-κB2, factors STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B, STAT6, and protein SOCS2, was assessed by enzyme immunoassay. We also determined the concentration of TNFα, IL-1β, TGFb, IFNα, IFNβ, IFNγ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-17A, RAIL-1, RANTES. The results of this study indicate that the stage of pneumonia convalescence is accompanied by dysregulation of the production of the main proinflammatory cytokines, manifested by a decrease in the level of TNFα, TGFb, RANTES, IL-4, IL-17A, IFNβ, IFNγ and an increase in the production of IL-2 and IFNα. Against this background, a decrease in the phosphorylation of the STAT3 and STAT4 factors was noted, as well as a decrease in the content of p50 and p65 proteins in MNCs. These changes were associated with an increased content of the SOCS2 factor in MNCs. The analysis showed that an increase in the content of SOCS2 in MNCs from the minimum level determined by the concentration corresponding to the 1st quartile of the sample (1.3 ng / ml) to the maximum, determined by the 4th quartile of the sample (1.7 ng / ml) is associated with a decrease in production IL-1β, IL-4, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-17A, TGFb, RANTES and IFNβ against the background of an increase in the level of INFα, INFγ and IL-2. Changes in cytokine production were accompanied by an increase in STAT5B, STAT4, and NF-kB2 levels and a decrease in STAT3 phosphorylation. a decrease in the content in the cell of the components of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB, in particular, p50, p65. Conclusion. The peculiarities of the relationship of SOCS2 with the studied factors suggests that its high level helps to limit the production of proinflammatory cytokines, in particular those produced by type 2 T-helpers and Th17, stimulates an increase in ICC sensitivity to IL-2 and stimulation of type 1 T-helpers. These effects are realized due to an increase in the phosphorylation of the STAT5 and STAT4 factors, a decrease in the STAT3 activity, and a change in the ratio of the components p50, p65 and NF-κB2 of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB in the cell.
Aim to determine the clinical and laboratory relationships of the level of soluble stimulating growth factor expressed by genome 2 (sST2) with indicators characterizing the development of cardiovascular pathology in patients with spondyloarthritis (SPA). Materials and methods. A total of 46 patients aged 39.2 ± 10.2 years with SpA (including 40 (87 %) with ankylosing spondylitis, 6 (13 %) with psoriatic arthritis) were examined. There were 36 (78.3 %) males, 10 (21.7 %) females among the enrolled patients. 27 (84.4 %) of 32 examined patients had HLA-B27. To assess the disease activity the BASDAI and ASDAS scores were used, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein values were measured; the levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), N-terminal fragment of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), sST2 in blood serum were evaluated. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors, aortic pulse wave velocity (PWVAo), the results of standard electrocardiography, transthoracic echocardiography, carotid duplex ultrasonography were assessed. Results. The mean sST2 level was 33.34±11.2 ng/ml, an sST2 concentration above the threshold value was found in 19 (41.3 %) patients. No significant relationships between serum sST2 level and disease activity indicators, echocardiographic parameters, rhythm and/or conduction disturbances on electrocardiograms were found. A higher PWVAo was noted in patients with sST2 level above the average (p=0.036); the level of NT-proBNP was more often increased in patients with high levels of sST2 (p=0.085). Higher sST2 concentrations were found in patients treated with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs due to the high disease activity (р=0.039). Conclusion. An increase in sST2 levels was found in 41.3 % of patients with SpA. An increase in serum sST2 concentration is associated with an elevated PWVAo and an increase in the level of NT-proBNP, which may indicate incipient cardiac remodeling, cardiac fibrosis, and the initial stages of the development of heart failure. The new data obtained indicate the advisability of planning and performing larger prospective studies of patients with SpA for the early detection of preclinical signs of damage to the cardiovascular system, cardiac remodeling, and assessment of the effectiveness of therapy.
ANALYSIS OF CLINICAL CASES
Cardiomyopathy syndrome (stress-cardiomyopathy) is an acute reversible systolic dysfunction of left (or rare right) ventricle without stenotic atherosclerosis and/or thrombosis of coronary artery. We are presenting a case of stress-cardiomyopathy after the neurosurgery. Aim: The aim of this observation is to demonstrate a case of takotsubo syndrome in a young patient in the early postoperative period. Key points: A 21-years-old woman was hospitalized in the neurosurgery department. Hospitalization was performed due to persistent pain in the left elbow joint with irradiation to left 4 & 5 hand fingers as well as dysfunction of the left elbow joint, as a result of previous surgical intervention for a fracture one year before. Due to the lack of a positive effect from conservative therapy, it was decided to conduct a second surgical treatment. Decompression of the left ulnar nerve was performed at the level of the cubital canal with its transposition. This was complicated by the development of takotsubo syndrome in the postoperative period, confirmed by echocardiography, ECG, as well as the absence of atherosclerotic changes in the coronary artery according to coronary angiography. Conclusion: The early postoperative period may complicate of development of takotsubo syndrome, in the neurosurgical operations and in the young age too.
This article presents the features of the course of liver cirrhosis (LC) in a patient with a new coronavirus infection. The patient had no specific respiratory symptoms of COVID-19 (CoronaVirus Disease 2019), and the reason for outpatient examination for SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) RNA was the presence of these symptoms in relatives. Previously, patient E. had been undergoing in-patient examination and treatment for abdomen volume build-up against the background of prolonged alcoholization, and was diagnosed with alcoholic class B LC according to Child-Pugh classification. Conservative therapy was administered, and the patient was discharged with regression of ascites. Within a week after SARS-CoV-2 identification, patient E. showed signs of LC decompensation in the form of increasing abdominal volume, which required repeated inpatient treatment, during which portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and progression of chronic liver disease (CLD) in the post-coid period were revealed. Literature data on 30-day mortality in patients with LC against COVID-19 background are presented, as well as my own observations on the example of 580 case histories. Complications of new coronavirus infection in patients with CLD, methods of their correction are considered here. This observation demonstrates the social significance of the problem of COVID-19 incidence in patients with LC, the necessity for screening for COVID-19 in case of the presence of decompensation episodes, as well as active prevention of infection in these patients.
ISSN 2411-6564 (Online)