LECTURES
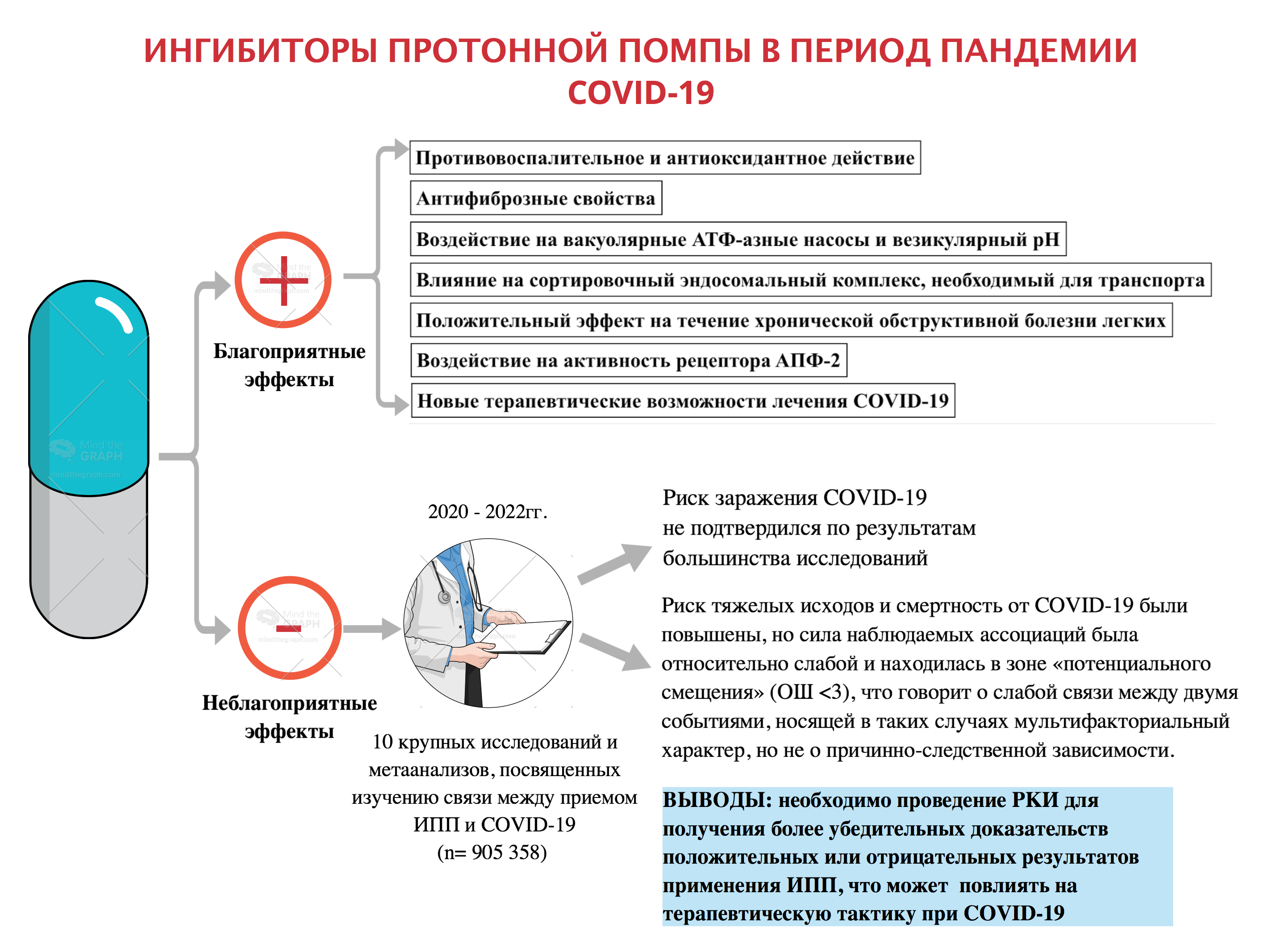
The safety of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) use in coronavirus infection (COVID-19) is not well understood. PPIs are potent suppressors of gastric secretion and become one of the ten most widely used drugs in the world. They are expected to influence virus susceptibility, severity, and outcomes in patients diagnosed with COVID-19. This concern is based on their mechanism of action — suppression of gastric acidity, which is considered the first line of defense against infections. Taken together, the results of most studies and meta-analyses support that PPIs use has been associated with increased risk of COVID-19 and severe outcomes. However, taking into account all potential risk factors for disease severity seems impossible in the real world in the context of COVID-19, so conclusions about causal relationships between PPI use and COVID-19 should be treated with great caution. An additional interesting point about the use of PPIs in the pandemic is that it reduced absorption of certain vitamins. On the other hand, several studies have appeared in the literature regarding the protective therapeutic effects of PPIs. There is growing evidence of an immunomodulatory and antifibrotic role of PPIs that could be used in the treatment of COVID-19. In addition, their ability to alkalize the contents of endosomes and lysosomes serves as an obstacle to the penetration of the virus into host cells. This review analyzes the possible effects of PPIs in patients with COVID-19.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Osteoporosis is a widespread metabolic disease of the skeleton among the elderly. Osteoporotic fractures are significant manifestation of the disease, which can substantially affect the quality of life. The purpose of this article is to review approaches to the management of patients with acute osteoporotic fracture. This article consists of two parts. The first part reviews general information about osteoporosis, clinical course of osteoporotic fracture, differential diagnosis of pain syndrome, methods of visualization of fractures, differential diagnosis of osteoporosis. In the second part, we discuss differential diagnosis of osteoporotic fracture according to the data of imaging methods, non-pharmacologic, pharmacologic and surgical methods of treatment.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a severe, progressive lung disease of unknown etiology with an average worldwide prevalence of 15 per 100,000. According to the etiology, IPF is classified into sporadic, syndromic, and familial cases. Sporadic cases refer to multifactorial diseases and are associated with age, viral infections, smoking and inhalation of dust, contact with chemicals and drugs, gastroesophageal reflux disease. There were revealed an association of sporadic IPF with allelic variants of the genes AKAP13, ATP11A, DPP9, DSP, IVD, IL1RN, FAM13A, MUC5B, SFTPC, SPPL2C, TERC, TERT, TOLLIP. Syndromal IPF develops in German-Pudlak syndrome. Familial cases of the disease are caused by mutations in the genes encoding surfactant (SFTPC), mucin (MUC5B), deadenylation nuclease (PARN), components of telomere functioning (RTEL1, TERC, TERT). In 2000, the American Thoracic Society recommended glucocorticoids and cytostatics for the treatment of ELISA in order to influence the inflammatory process due to the activation of fibroblasts and their accumulation in the extracellular matrix of the lungs. These recommendations are still used by many doctors, despite the publication of reliable data on the increased mortality and hospitalizations of IPF patients taking prednisolone and azathioprine. According to recent meta-analyzes, pirfenidone (an inhibitor of the synthesis of procollagen I and II growth factors) and nintenadib (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor) are the most effective treatments for IPF. Since genetic factors play an important role in the etiopathogenesis of the disease, it is promising to search for methods of targeted therapy for IPF using specific noncoding RNAs as targets, changes in the expression of which are not specific of other bronchopulmonary diseases. These RNAs include miR-9-5p, miR-27b, miR-153, miR-184, miR-326, miR-374, miR-489, miR-630, miR-1343 (decreased expression in IPF); miR-340, miR-424, miR-487b, miR-493, lncRNA AP003419.16, lncRNA AP003419.16 (increased expression in IPF).
The incidence of different psychiatric disorders (affective, anxious, dysmorphic, psychotic) during menstruation, pregnancy and the postpartum period reaches 80 %. Mental disorders are risk factors for the delayed onset and shortening of menstruations, manifestation of the premenstrual syndrome (PMS), inadequate emotional reactions during menstruations, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, decreased regularity and satisfaction of sexual activity, fertility, pregnancy failure, reduction of the lactation period, early onset of menopause with long duration and clinical severity of premenopause, etc. An individual approach to treatment should take into account risk factors (heredity, comorbid disorders, sex, age, etc.) of adverse events (AD), the balance of efficacy and safety of drugs
The incidence of ulcerative colitis has been increasing in recent years, and its manifestation at a young age has become a trend that is prognostically unfavorable. The clinical picture of ulcerative colitis is often vague, which leads to an initially erroneous diagnosis. One of the main problems is to assess the effectiveness of treatment and the risk of recurrence of ulcerative colitis, which requires invasive intervention. The aim of the study was to analyze the data of modern scientific literature on noninvasive biomarkers of ulcerative colitis. The data of foreign and domestic articles on the research topic published in Pubmed and eLibrary over the past 5-10 years are analyzed. Biomarkers of neutrophil origin are a promising direction in the primary diagnosis and assessment of ulcerative colitis activity.
Cardiovascular diseases are the second leading cause of death and disability worldwide after malignancies. Heart failure (HF) has a large impact not only on the economics of healthcare but also on the quality of life, functionality and life expectancy of patients. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies have been developed, but these medical therapies have limited effects to cure patients with severe CH. Heart transplantation is limited due to the low number of donor organs. Human cardiac potential for spontaneous repair is insignificant, so regenerative therapy is in great demand as a new treatment strategy. Currently, there are several strategies for heart regeneration. Transplantation of somatic stem cells was safe and modestly improved cardiac function after myocardial infarction and in patients with CF mainly through paracrine mechanisms. Alternatively, new cardiomyocytes could be generated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to transplant into injured hearts. However, several issues remain to be resolved prior to using iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, such as a potential risk of tumorigenesis and poor survival of transplanted cells in the injured heart. Recently, direct cardiac cell-free reprogramming has emerged as a novel technology to regenerate damaged myocardium by directly converting endogenous cardiac fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocyte-like cells to restore cardiac function. Many researchers have reported direct reprogramming of the heart in vivo in animal and human cells. In this review, we review the current status of cardiac cell-based and cell-free regenerative technology, a great hope to treat cardiovascular diseases in clinical practice.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Background: assessment of type, prevalence and duration of residual symptoms after COVID-19 in recent studies is controversial because of differences in design. Aim: to assess the prevalence and severity of symptoms in the long-term period after COVID-19. Materials and methods: patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the period 13.04.2020-10.06.2020 were interviewed by phone: 195 (58,2 %) convalescents at 143 (131-154) days after disease onset and 183 (54,6 % ) of them at 340 (325-351) days. Results: The subjective assessment of health status with 100-point scale before and after the COVID-19 was 95 (80-100) and 80 (70-96) points, p< 0,001, at first interview; 90 (80-100) and 80 (60-90) points, p< 0,001, at second one. Various complaints were detected in 63 % of respondents at the first interview and in 75 % at the second, the number of identified symptoms was 2 (0-6) and 4 (1-8) respectively. The most frequent complaints were weakness/fatigue (31.3 and 47.5 % of respondents), joint pain (31.3 and 47.5 %) and dyspnoe/shortness of breath (31.3 and 43.2 %). The growth of these indicators can be associated with a change in the interview methodology. The severity of the symptoms at second interview was low: fatigue — 3 (0-6) points, shortness of breath — 0 (0-3) points; joint pain, weakness and dyspnoe — 0 (0-5) points each. Conclusion: a decrease of health status can sustain for a long time after COVID-19. Symptoms persist in a significant proportion of convalescents, but their severity in the end of follow-up is quite low.
Background. According to the scientific literature, anti-CD74 IgA antibodies (IgA anti-CD74) are considered as a possible marker for the diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (SpA). The level of IgA anti-CD74 in patients with back pain due to degenerative spine disease has not been studied. Therefore, it could be interesting to compare the serum levels of IgA anti-CD74 in patients with chronic back pain in various diseases. Aim: to compare the levels of IgA anti-CD74 in patients with SpA and degenerative spine diseases. Material and methods. A total of 87 SpA patients (55 male, mean age 41 [29; 49] years) fulfilling the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (2009) criteria for Axial SpA, and 39 patients (25 male, mean age 45 [34; 53] years) with neurologist-verified degenerative spine diseases (ICD 10 codes — M 51.1 and M 54.4) were enrolled to the study. The serum levels of IgA anti-CD74 were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in all patients. Results. The median levels of IgA anti-CD74 in patients with SpA were 11.3 [5.4; 19.4] U/ml, in patients with degenerative spine disease — 6.9 [4.5; 13.7] U/ml (p=0.024). IgA anti-CD74 serum levels were above the cut-off value in 58 (66.7 %) patients with SpA and only in 11 (28.2 %) patients with degenerative spine disease (p<0,001). The elevated serum levels of IgA anti-CD74 were detected in 10 (40 %) of 25 male patients and in 1 (7.1 %) of 14 female patients (p = 0.029, χ2 = 4.785) with degenerative spine disease. Conclusion. Serum levels of I gA anti-CD74 were increased in two-thirds of patients with SpA. IgA anti-CD74 was significantly higher in SpA patients compared to patients with degenerative spine disease. >< 0,001). The elevated serum levels of IgA anti-CD74 were detected in 10 (40 %) of 25 male patients and in 1 (7.1 %) of 14 female patients (p = 0.029, χ2 = 4.785) with degenerative spine disease. Conclusion. Serum levels of I gA anti-CD74 were increased in two-thirds of patients with SpA. IgA anti-CD74 was significantly higher in SpA patients compared to patients with degenerative spine disease.
ANALYSIS OF CLINICAL CASES
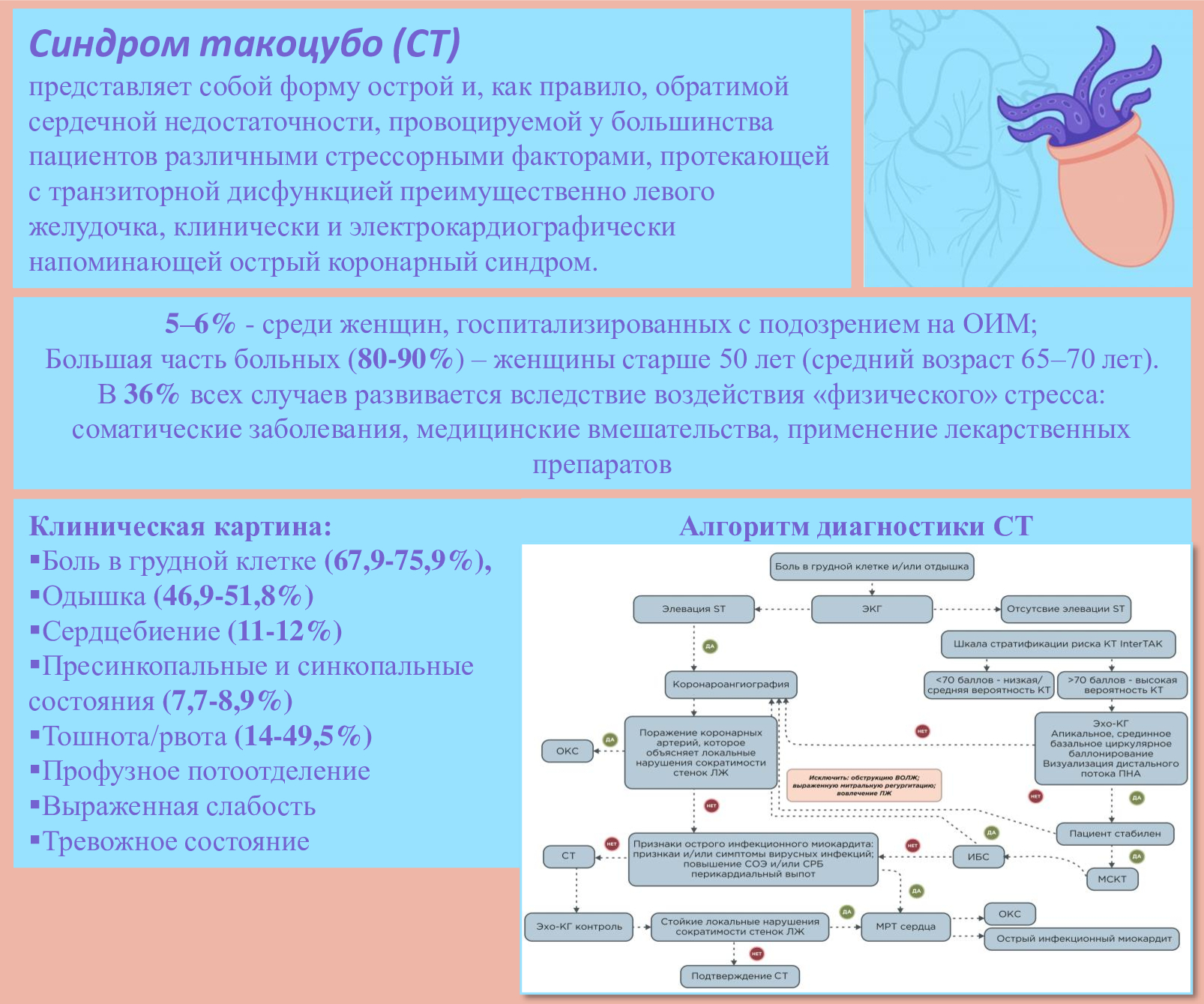
Takotsubo syndrome (TS) is an acute reversible left ventricular myocardial dysfunction caused by an emotional or physical trigger. In the perioperative period, TS is in some cases induced by various psychological factors, such as stress before/after surgery, and non-psychological factors, such as drug administration. This article describes the clinical observation of takotsubo syndrome that developed in the early postoperative period of rhinoplasty
ISSN 2411-6564 (Online)